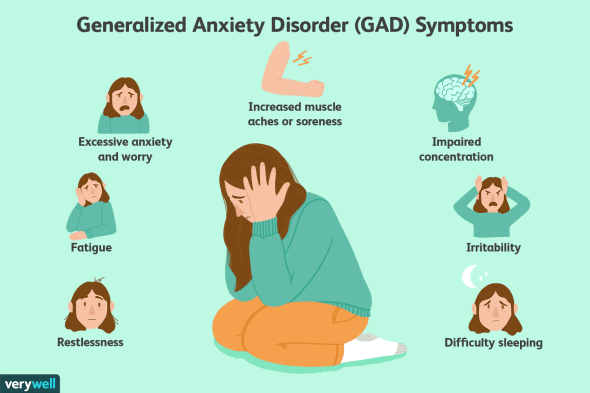
Anxiety is a common feeling. It’s your brain’s method of responding to stress and warning you about impending danger. Everyone experiences anxiety from time to time. When confronted with a difficulty at work, before taking a test, or before making a major choice, for example, you may feel concerned.
Anxiety is normal on occasion. Anxiety disorders, on the other hand, are distinct. They’re a collection of mental disorders that induce uncontrollable worry and terror. Excessive anxiety may cause you to avoid work, school, family gatherings, and other social settings that may exacerbate or provoke your symptoms. Many persons with anxiety problems can learn to control their emotions with the right treatment.
Anxiety is a natural response to stress that can be useful in some circumstances. It can warn us of impending risks and assist us in planning and paying attention. Anxiety disorders are marked by excessive fear or worry instead of typical sensations of uneasiness or anxiety. Anxiety disorders are the most prevalent mental illnesses, afflicting almost one-third of all people at some time in their life. On the other hand, anxiety disorders are curable, and there are a variety of effective therapies available. The majority of persons who receive treatment are able to live regular, productive lives.
Anxiety is characterized by muscular tension and avoidance behavior in anticipation of a future worry. Fear is an emotional response to an impending threat that is more commonly linked with a fight or flight response – remaining to fight or fleeing to avoid danger. People with anxiety disorders may strive to avoid circumstances that trigger or exacerbate their symptoms. Workplace performance, schoolwork, and personal relationships may all be impacted.
Different Types of Anxiety
Here is the latest list of all types of anxiety that you should know about.
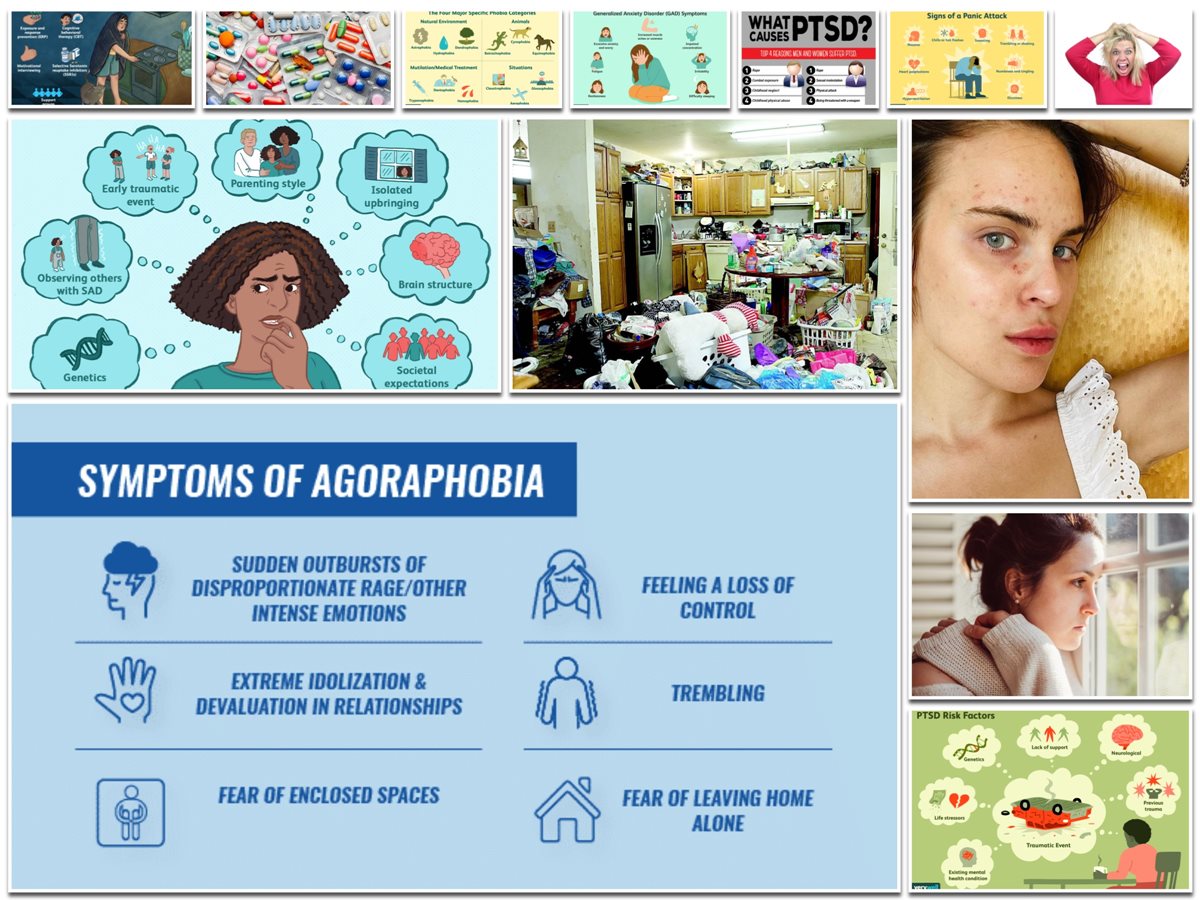
1. Generalized Anxiety Disorder
GAD (Generalized Anxiety Condition) is an anxiety disorder marked by persistent anxiety, excessive concern, and tension, even when there is little or no cause for it.
2. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
OCD is an anxiety condition marked by persistent, unwanted thoughts (obsessions) and/or repetitive actions (compulsions). Hand washing, counting, checking, and cleaning are common repetitive actions undertaken in the hopes of preventing or removing obsessive thoughts. However, executing these so-called “rituals” only gives short respite, and failing to do so significantly increases anxiety.
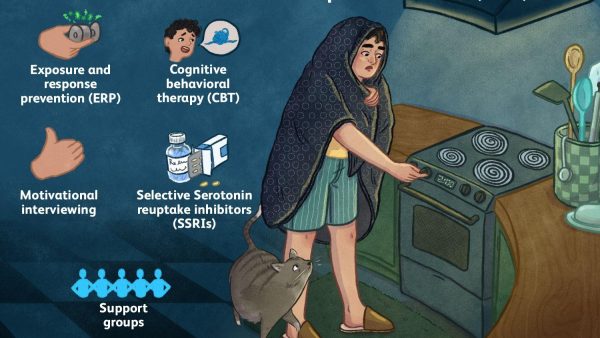
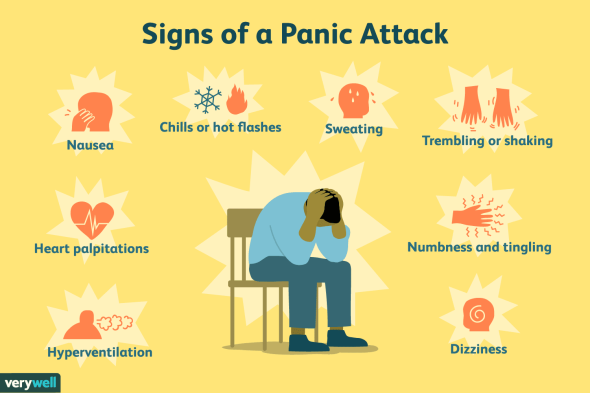
3. Panic Disorder
Panic disorder is an anxiety condition marked by sudden and recurrent bouts of acute terror and physical symptoms such as chest pain, heart palpitations, shortness of breath, dizziness, or stomach discomfort.
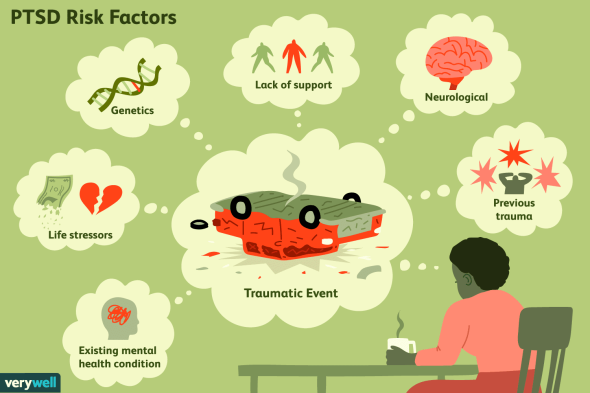
4. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
PTSD is an anxiety condition that can develop after being exposed to a scary incident or encounter in which significant bodily damage happened or was threatened. Violent personal attacks, natural or human-caused disasters, accidents, or military conflict are all examples of traumatic events that can lead to PTSD.
5. Social Phobia (Or Social Anxiety Disorder)
Anxiety condition characterized by extreme anxiety and excessive self-consciousness in ordinary social interactions is known as social phobia. Social phobia can be restricted to a single scenario – such as a fear of speaking in official or informal settings, or of eating or drinking in front of others – or, in its most extreme form, can manifest itself practically wherever a person is among other people.
6. Specific Phobias
You have a strong aversion to a certain thing or circumstance, such as heights or flying. Fear may drive you to avoid everyday circumstances if it goes beyond what is appropriate.
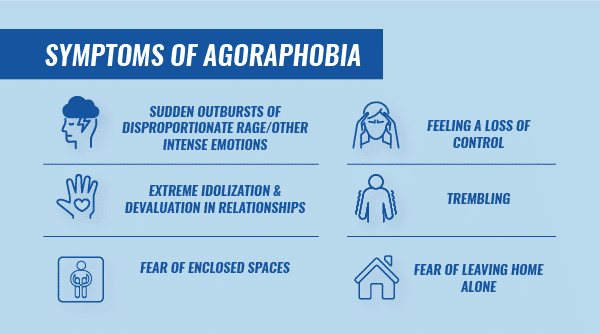
7. Agoraphobia
You have a strong aversion to being in a situation where it appears difficult to flee or obtain aid in the event of an emergency. When you’re on a flight, on public transit, or standing in line with a crowd, for example, you could panic or feel nervous.
8. Separation Anxiety
When a loved one departs, children aren’t the only ones who are afraid or nervous. Separation anxiety disorder may affect anyone. If you do, you’ll be worried or afraid when someone you care about leaves your sight. You’ll be concerned that something awful will happen to your loved one at any time.
9. Selective Mutism
This is a form of social anxiety in which young children who spoke regularly with their families do not converse in public, such as at school.
10. Medication
Anxiety condition that has been induced. Some symptoms of anxiety disorder can be triggered by the use of certain pharmaceuticals or illicit drugs, or by the withdrawal from certain drugs.
11. Skin-Picking
Dermatillomania is the medical term for skin-picking. It’s an impulse control problem in which you pick at your skin on a daily basis and have a hard time stopping yourself. Bleeding, bruising, and scarring are all possible consequences. Picking the skin on your face is typical, but other parts of your body may be picked as well. Skin plucking is believed to be a form of addiction. Or that it calms and relaxes you. OCD and dermatillomania are frequently co-occurring disorders. Your GP may refer you to a psychiatrist or another specialised mental health practitioner for diagnosis and therapy.
12. Trichotillomania (Hair Pulling)
Trichotillomania is a medical term for hair pulling, an impulse control issue. If you suffer from this disease, you will find it difficult to resist the temptation to pull your hair out. It might come from your scalp or from other parts of your body, such as your arms, eyelashes, eyebrows, legs, or pubic region. You may feel a build-up of tension that you can relieve by pulling your hair out. Pulling hair out may provide relief or pleasure, or you may be completely unaware of your actions.
Stopping this behavior, which may lead to hair loss and emotional discomfort, can be tough. This may make you feel guilty or ashamed, and may have an impact on how you feel about yourself or how others see you. Other specified anxiety disorder and unidentified anxiety disorder are words for anxiety or phobias that don’t match the exact criteria for any of the other anxiety disorders but are bothersome and disruptive enough to warrant treatment. Anxiety disorder induced by a medical disease involves severe anxiety or panic triggered directly by a physical health issue.
13. Hoarding Disorder
Hoarding disorder is characterized by a persistent inability to let go of belongings and an unhealthy connection to even little stuff. It might result in an overabundance of belongings (or animals) and a crowded living environment. You may assign feeling to inanimate objects, develop deep sentimental attachments to them, or see the use in any object. These ideas may cause you to experience worry, guilt, or grief when you discard stuff.
14. Trauma
Trauma and stress-related disorders are two types of stress-related disorders. They are linked to a traumatic or tragic event (for example, a loved one’s untimely death, a vehicle accident, or a violent occurrence such as war or sexual assault) or a stressor (e.g., divorce, beginning college, moving). The most prevalent kind of trauma and stress-related condition is post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Obsessions and compulsions linked to disease, such as studying symptoms or checking to see whether you have them, are common indicators of health anxiety. It’s a symptom of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) is a condition in which you have obsessive and compulsive thoughts about your looks. For additional information, see our BDD site.
Perinatal anxiety, also known as perinatal OCD, affects certain women during pregnancy or the first year following delivery.