Figurative language is the use of words in a non-traditional sequence and meaning to express a complex meaning, colorful writing, clarity, or evocative contrast. It use a common phrase to allude to something without explicitly expressing it. Reading the Management Discussion and Analysis (MD&A) requires an understanding of figurative language, since management may employ a metaphor to assist explain complex topics or the company’s direction.
Fiction authors employ figurative language to engage their readers with a more imaginative tone that prompts thought and, perhaps, laughter. It adds more intrigue and drama to fiction writing than literal language, which utilizes terms to relate to declarations of truth.
Different Types of Figurative Language
Figurative Language is a resource for exploring and expanding our understanding of figurative language, and to help everyone in the world communicate in more interesting and effective ways. This article is a reference to help students and teachers find figurative language and understand its meaning and use. Here is the list of all types of figurative language that you should know about.
1. Metaphor
Metaphor is used to compare things in the same way as a simile is, but without the connecting words. “Life is a rollercoaster,” for instance.
Other examples of metaphors include:
- The fighter has a stone heart.
- It’s a battleground when it comes to love.
- You are my sunshine, baby.
- The legislator’s best friend is chaos.
- I’m suffocating in a sea of sadness.
- My roommate is experiencing a wide range of emotions.
2. Alliteration
Alliteration is a figure of speech in which the first consonants of adjacent words are repeated. “Sheep should sleep in a shed,” for example.
Examples:
- The pitter-patter of paws startled me up from my nap as it reverberated down the corridor.
- My ears were scorched by the clamorous crash of stones cracking on the concrete.
- Old creaking containers are poised to break open, containing a lifetime’s worth of dust.
- My ears are filled with delight as I listen to the chatter of babies.
3. Hyperbole
Hyperbole exaggerates to emphasise or create a larger impression. “He runs quicker than the wind,” for example.
Examples:
- I’m so hungry right now that I’d eat dirt.
- My brother is the equivalent of a skyscraper in height.
- The performance was so loud that the drums reverberated throughout the venue.
- For me, getting through the day was like running a marathon.
4. Irony
When there is a disconnect between what is stated and what is meant, irony is utilized. “The police station is robbed,” for example.
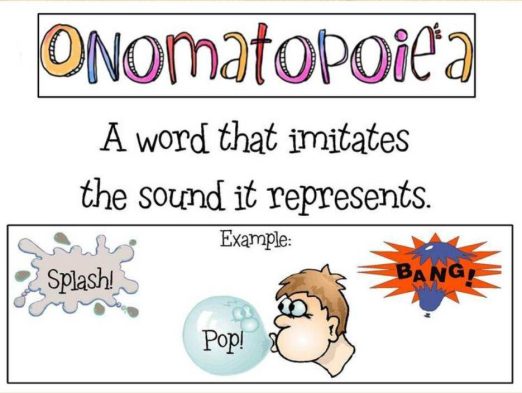
5. Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia is the use of words that sound like the thing being described. Machine noises like zap and boing and animal sounds like moo and ribbit are instances of this.
Onomatopoeia can be found in the following examples:
- The heater in the fireplace hissed and cracked.
- As it ascended the slope, the truck’s engine roared.
- When I went to the restroom, the alarm clock went off.
6. Personification
Personification refers to the use of human characteristics to characterize non-living objects or concepts. Personification is exemplified by the phrase “the flowers danced in the breeze.”
Personification can also be seen in the following examples:
- The cruelest month of the year is April.
- The radio locked its gaze on me.
- Throughout the drive, the vehicle brakes screeched.
- With a groaning protest, the vehicle came to a halt.
7. Synecdoche
Synecdoche is another figure of speech. When a portion is represented by a whole or vice versa, this occurs. Synecdoche may be seen in the phrase “all hands on deck.” The term “hands” refers to a member of a team.
Other examples of synecdoche include:
- Bread can refer to either food in general or money in particular.
- The term “head” can apply to either livestock or people.
- Workers might be referred to as hired hands.
8. Apostrophe
When a speaker addresses someone (or something) who isn’t there or can’t react in real life, he or she uses an apostrophe. The person being addressed might be alive, deceased, or fictional.
9. Allusion
When a text refers to another text”or a person, place, or event”it is known as allusion. It might be expressed directly or inferred from the context. “You’re my Achilles heel,” as an example of allusion, refers to a vulnerability one may have for someone.
Examples:
- When you took his sweets, you stole the forbidden fruit.
- He didn’t do anything nearly as heinous as down a cherry tree.
- She was the class’s Helen of Troy, forcing all of the males to fight.
- When my young child snatched my lipstick, she bolted quicker than a racing bullet.
10. Oxymoron
When two phrases that contradict one other are combined, it is called an oxymoron. An example of an oxymoron is the phrase “bittersweet.” Bitter and sweet are two opposite emotions or states of being.
Examples:
- My father’s rash decision resulted in his being stranded in the middle of the lake without a life jacket.
- Customers rave about the huge shrimp.
- He is kept awake by the night’s deafening quiet.
- The river cuts through the trees, an ever-flowing calm of water.
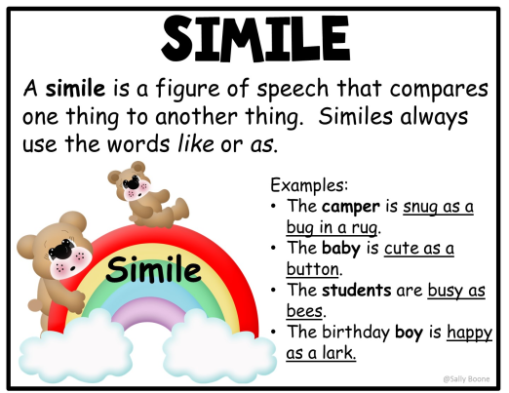
11. Simile
A simile is a figure of speech that compares two dissimilar objects using the terms “like” or “as,” and it is often employed in everyday conversation. A simile is a metaphor that is utilized to make an intriguing link in the imagination of the reader.
“The cat sat in the chair like a king surveying his kingdom,” for example, is a simile. The cat’s sitting position is likened to that of a king who unwinds in a unique chair intended only for him and no one else in the realm.
Examples:
- My mother is buzzing like a bee.
- They battled like a pack of wolves.
- My dog’s bark is as thunderous as it gets.
- Her devotion to her children is as unwavering as the passage of time.
- The eyes of your child are brighter than the stars.
12. Symbolism
When a term has its own meaning but is used to signify something completely distinct, this is known as symbolism.
In everyday life, examples include:
- The American flag is used to signify patriotism and affection for one’s nation.
- Using a crimson rose to signify love in your writing.
- An apple pie is used to symbolism a typical American way of life.
- A chalkboard is used to signify education.
- Using the color black as a symbol for evil or death in your work.
- An owl is used to signify wisdom.
13. Idiom
A popular term that has taken on a meaning other than its original meaning is known as an idiom. Idiomatic phrases differ depending on the culture and language. They are sometimes difficult for language learners to understand since the real meaning of the term is so different from what is being communicated.
Examples:
- Because of my grandmother’s green thumb, her garden is prospering.
- Because it was raining cats and dogs outside, the kids couldn’t play baseball.
- To win in life’s game, you must play your cards correctly.
Some people give up before they should and never understand the value of putting in the effort required for success.
14. Cliché
A cliché is a phrase, statement, or concept that has lost its original meaning or effect due to overuse. Because of their regularity, clichés may be unpleasant and frustrating at times.
15. Euphemism
When a polite or mild phrase or statement is used in lieu of something more unpleasant, offensive, or forbidden, it is referred to as a euphemism. In this way, it’s the polar opposite of exaggeration.
16. Assonance
Alliteration and assonance are related. In this situation, though, vowel sounds are repeated in your sentences.
17. Consonance
Consonance is similar to assonance, except the emphasis is now on repeated consonant sounds.
18. Puns
Puns are a type of figurative language in which a play on words is created. They give a subject a deeper meaning and are frequently used as a joke or to be funny.
19. Litotes
Litotes are figures of speech that communicate a message by being understated. It has a sardonic tone to it. By negating the contrary, the assertion is confirmed.
Examples:
- I can’t say I disagree with your point of view.
- My dog isn’t the nicest of creatures.
- After staying up all night watching television, he’s not even a bit weary.